Fatty Liver Disease: Causes, Risk and Prevention
Last updated on February 3rd, 2025 at 11:07 am
Introduction and prevalence of fatty liver disease
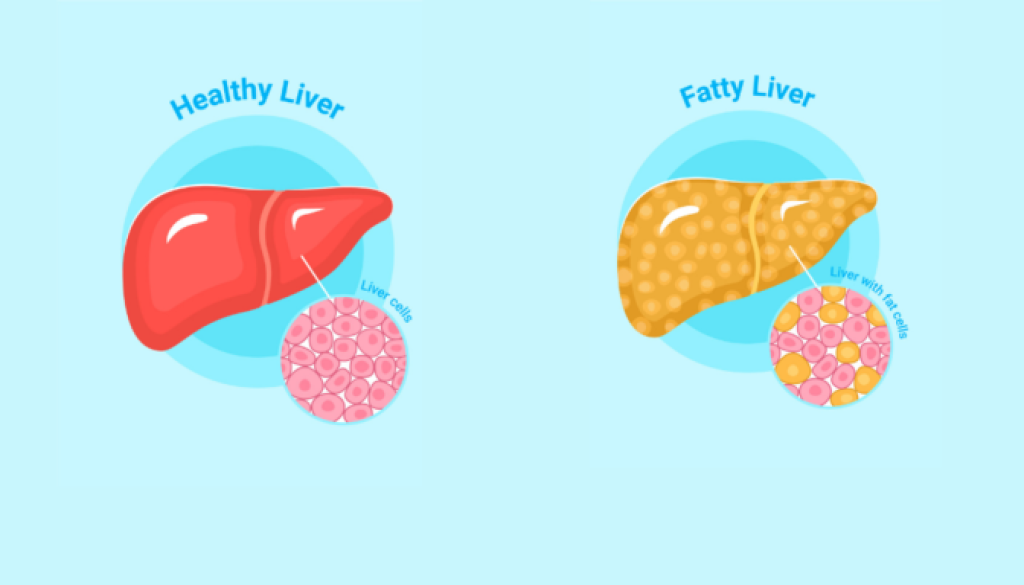
Fatty liver disease is a non-transferable condition caused by excess storage of fat in the liver(it is important to note that a small amount of fat in the liver isn’t bad but if the weight of fat reaches 5-10% of total liver weight, then it becomes a problem.).
Our liver serves many functions such as digesting foods, storing energy, and removing poison, therefore, it is really important to take care of them to avoid any future problems.
The fatty liver itself doesn’t cause any immediate problems but, it further causes liver damage.
Survey taken by medical professionals showed that cases of fatty liver have increased from 391.2 million in 1990 to 882.1 million in 2017.
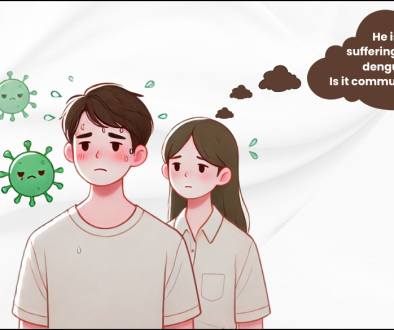
Nepal isn’t an exception to this disease too. Many men and women are suffering from fatty liver disease in Nepal. But this condition can be prevented or reversed through some lifestyle changes.
Is it a transferable disease?
Fear not, this disease is not transferable from person to person i.e. there is no reason for you to avoid other people.
What causes fatty liver disease?

There are many likely causes of fatty liver disease, some of them are listed and explained below:
- Drinking alcohol excessively: Drinking excessively can cause liver metabolism to change which can lead increase in fat in the liver and causes AFLD(Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease).
- Obesity is another cause of NAFLD(Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease). Being overweight can lead to an increase in the amount of fat in the liver.
- Type 2 diabetes and/or insulin resistance are other likely causes of NAFLD.
- An excessive amount of fat in the bloodstream can also cause NAFLD.
- Metabolic Syndrome(is a condition which is caused by high blood pressure, blood sugar level, excess fat around the waist area, etc.) is another cause of NAFLD. Etc.
Who is at most risk?
People who fall into any one or all of the following category is most at risk of FLD(Fatty Liver Disease).
- People who drink excessively are highly likely to develop this disease
- Asian people are more likely to get this disease than western society(but that doesn’t mean western society is immune to this disease)
- People, who are obese, with an excessive amount of belly fat are highly likely to get this disease
- People with type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and high blood sugar level is highly at risk
- People of older age are more likely to get this disease than people of young age
- A woman going through a menopausal phase
- People who are suffering from sleep apnea
- People who are malnourished, etc.
What are the symptoms of fatty liver disease?
Usually, people with this disease show no symptoms until the later stages of this disease.
But, if you feel any or all of the following symptoms, it is highly likely you are suffering from this disease.
- Swollen belly(Abdominal pain),
- Weight loss, nausea, or loss of appetite,
- Jaundice related symptoms(such as yellowish skin, etc.),
- Huge breasts in men,
- Larger than normal blood vessels in the skin, etc.
When is it time to see a doctor?

If you have felt/shown any or all of the symptoms given above(for a week or more) OR you belong to the most at-risk group, you should go see a doctor.
A Hepatologist is a doctor that specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases and problems related to the liver, bile ducts, gall bladder, and pancreas. Therefore, you can consult with a Hepatologist, if you suspect you have fatty liver or diseases related to it.
Request an appointment with a hepatologist>>>
Make Appointment
Treatment
For people who are suffering from this disease, there is good news.
If you follow your doctor’s directive, you will likely be able to reverse this disease. So, DO AS YOUR DOCTOR SAYS!
Your doctor will prescribe medication for treatment as per tests conducted.
See available doctors at Clinic One>>>
Prevention
This disease can be prevented by following a healthy lifestyle such as:
- Eating healthy and regular exercise
- Stop drinking excessive alcohol
- Drink plenty of water
- Taking medication for diseases that causes fatty liver disease(such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, high blood pressure, insulin resistance, etc.)