HPV Infection and Cervical Cancer
Last updated on January 6th, 2021 at 10:02 am
(HPV) Human Papillomavirus infection is a sexually transmitted infection that affects the reproductive parts of both men and women. About 90% of HPV is harmless which lingers for only about 2 months and clears by 2 years. But, some HPV can progress and cause cervical cancer (More on this later).
It has lead to many infectious cases, and in worst cases, even death, in Nepal as well as the whole world. So, it is crucial for us to understand, What it is? How is it transmitted? And other information related to it.
Relationship between HPV and Cervical Cancer
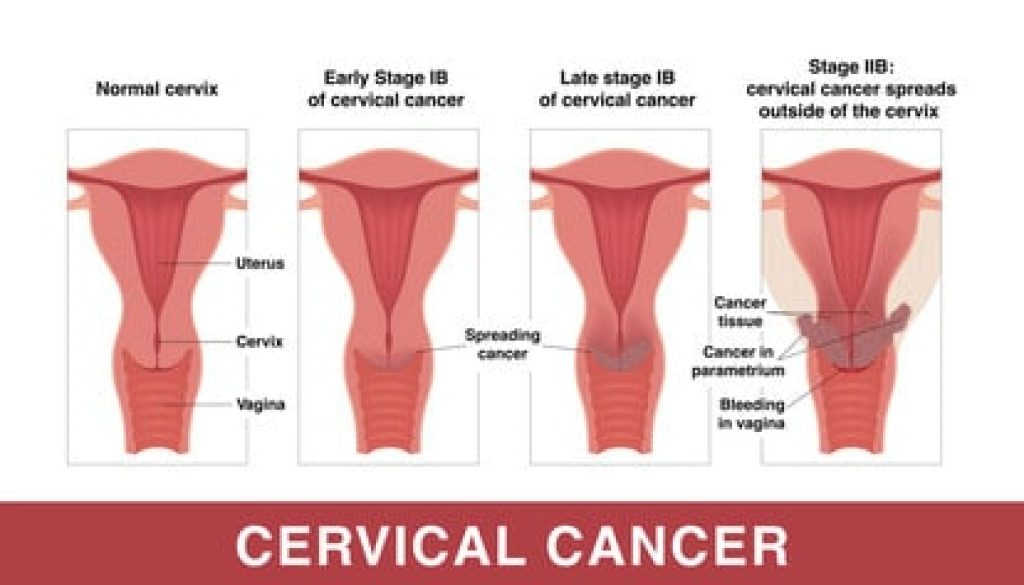
Cervical cancer is one of the most common diseases which is caused by HPV, most commonly in women. Nearly, all cervical cancer is directly attributable to HPV. It can take 15 – 20 years for a healthy woman to develop this cancer but, a woman with a weakened immune system can develop it in 5 – 10 years.
Causes and symptoms of cervical cancer

It begins when a healthy cervix cell is changed by HPV. HPV causes healthy cells’ DNA to change which, if left untreated, can cause them to become cancer cells. When a healthy cell becomes a cancer cell, it doesn’t follow its original life cycle(i.e does not die and multiplies continuously) which leads to forming a tumor. A cancer cell can tear from an infected area and grow in another area.
Normally, the early stages of cervical cancer do not show any kind of symptoms but, as it progresses it shows the following symptoms:
- Bleeding in between menstrual periods,
- Bleeding in sexual intercourse,
- Bloody, watery discharge having a foul smell,
- Having pelvic pain or pain during intercourse.
So, if you feel any or all of the symptoms mentioned above, please consult a doctor immediately.
How is HPV transmitted? What are its symptoms?
HPV infection is a viral disease/infection which is, generally, transmitted through sexual intercourse. It is not necessary to have penetrative sex to contract this infection. It can be transmitted through sex(vaginal, anal, or oral) with an infected person. Any sexually active person can contract this infection, even if they have sex with only one person. Normally, your immune system takes care of this infection but, if it was high-risk related HPV, it can progress and show symptoms including the following:
- Genital warts: These are flat lesions, having a cauliflower-like appearance, which mainly occurs in reproductive parts of both male and female
- Common warts: These are flat lesions having a rough appearance and raised like a bump, which mainly occurs in hands and fingers.
- Plantar warts: These are hard, grainy bumps that usually occur in the foot and/or fingers of the foot.
- Flat warts: These are flat-topped, slightly raised lesions that normally, occur in the beard area in men, occur in the leg in women, and on the face, in children.
If you or any member of your family shows symptoms mentioned above, please consult a doctor to vaccinate and properly manage such infections.
Prevention and Vaccination
Following are the prevention methods for cervical cancer:
1. Testing for HPV(Human Papilloma Virus) Infection
HPV test: A cell from the cervix area or vagina of a woman is taken and tested for strains of HPV.
Pap Smear test: This test is mainly done to find out the early stages of cervical cancer and prevent it. Cells from the cervix area are taken and tested for strains of HPV that cause cervical cancer. It may be performed along with an HPV test.
Learn more about Pap Smear Test here>>>
Visual inspection with acetic acid: In this test, a dilution of vinegar is applied to the cervix area, which turns white when exposed to vinegar, then the health care worker checks for any abnormalities. This test is very useful when there is a lack of a medical care system.
2. HPV Vaccination and its Importance

About 80% of people are infected by HPV in their life, so early vaccination can help protect and prevent diseases like Cervical Cancer caused by HPV.
According to the CDC, it is recommended that both men and women should get the HPV vaccine. HPV can affect both men and women.
The schedule for vaccination of HPV is given below:
- 2 doses:
- For children between age 9-10(early vaccination)
- For children between age 11-12(right age for vaccination)
- For children between age 13-14(late vaccination)
- 3 doses:
- For children and adults between age 15-26
- It is important to note that
- 2 doses are done in 0, 6 to 12 months schedule(i.e 2nd dosage is given 6 to 12 months after the 1st dosage.). The minimum time for a time interval between 1st and 2nd dosage is 5 months. If a vaccine is administered between a shorter period than 5 months, a third dosage is necessary between a minimum time of 12 weeks between the second and third dosage.
- 3 doses are administered in 0, 1 to 2 months, 6 months schedule(i.e second dosage is given in 1-2 months after the first dosage and the third dosage is given in 6 months after the second dosage). The minimum interval for 1st and 2nd dosage is 4 weeks, for 2nd and 3rd is 12 weeks, and for 1st and 3rd dosage is 5 months. If a vaccine is given in less interval than the minimum time, another dosage of vaccine is necessary after the elapse of the minimum period after the previous dosage.
- If the vaccine schedule is not followed due to any reason, dosage(already given) does not need to be repeated i.e have no maximum period for vaccination.
- It is also important to note that the vaccine is not recommended for a pregnant woman or person who is seriously ill. Also, if you have any allergies, please contact a doctor for a proper prescription.
- If a person shows positive for HPV, dosage as per the doctor’s prescription is recommended.
- According to the CDC, vaccination against HPV can help prevent about 90% of cancers caused by HPV from developing(including Cervical Cancer).
Other Preventative methods are:
- Having one sex partner
- Quitting smoking
- Delaying first sexual intercourse to late teen or early twenties,
- Using protection(condoms etc.) during sexual intercourse
- Avoiding sexual intercourse with people who have had many sexual partners, and so on.
Who is most at risk?
- People having HIV or other health problem which makes it hard for the body to fight other problems
- People who smoke
- People who have or has been using birth control pills for 5 or more years
- People who have given birth to 3 or more children
- People who have multiple sex partners
Cervical Cancer Fact Sheet
- As per WHO, there are more than 100 types of HPV, some of which(at least 14 of them) can lead to cancer. 16 and 18 HPV types can lead to cervical cancer and pre-cancerous lesions. Cervical cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in women, having 570000 estimated new cases in 2018 alone, representing about 7.5% of all cancer-related death of women.
- As per an article published by Kathmandu Model Hospital, one of the main causes of morbidity and mortality in Nepal as well as developing countries is Cervical cancer. According to the article, almost 34% of cases of cancer are related to it.
Challenges of Vaccination against HPV cases in Nepal
As per an article published by Kathmandu Model Hospital, even though vaccination against HPV can prevent its related diseases, challenges such as lack of proper parental guidance, reluctant adolescents, fear of promiscuity(having many sex partner) in teenagers, myths, and high cost, causes teenagers to not vaccinate.
So, it is really important to vaccinate and provide proper information related to this infection so that to encourage teenagers or adults to vaccinate properly to prevent such diseases.
Treatment of Cervical cancer
There are different types of treatment for cervical cancer, which are given below:
1. Surgery
It is a type of treatment that is used in the early stages of cervical cancer in which:
- Infected parts are cut away, or
- Cervix is removed, or
- Cervix and uterus both are removed.
2. Radiation Therapy
It is mainly used in locally advanced cervical cancer. It is also used when surgery does not stop such cancer.
It is a high-energy beam of light that is used to kill cancer cells. It is commonly used with chemotherapy as a primary treatment.
3. Chemotherapy
It is a type of treatment that uses chemicals/drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be introduced into the body through veins or pills.
For locally advanced cervical cancer small dosage of chemotherapy with radiation therapy is used.
It is used in high dosage for very advanced cancer cases.
4. Immunotherapy
It is a type of treatment that is used by providing your immune system with the strength, by taking prescribed drugs, to fight cancer cells. It is used when cancer is very advanced and other treatments are not working.
5. Supportive Care
This is a type of care that is provided with other treatments that are related to medical care for the mind to provide an extra layer of support to fight such cancer. A patient who is provided with this care feels better and may live longer.
This article has provided you with information that is related to HPV infection and cervical cancer prevention. If you or any member of your family have shown or are feeling the symptoms of both HPV and cervical cancer, please consult a doctor to prevent any progress of such diseases through vaccination or any other method.
Reference:
Human PapillomaVirus, WHO,
Human PapillomaVirus, MayoClinic,
Fact Sheet, CDC
Human PapillomaVirus, NHS UK
HPV Vaccination, CDC


